Agile Vs. Traditional Workflow: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the realm of project management methodologies, two prominent approaches stand out: Agile and traditional workflows. Each method has its own set of principles, practices, and benefits. In this blog, we'll delve into the key differences between Agile and traditional workflows, explore how an Agile workflow is created, highlight the advantages of Agile, and discuss how Stintar optimizes Agile workflows. We are offering a free Agile Project Management tool with CRM and HRM for up to 5 Users. (https://stintar.com)
Understanding Agile vs. Traditional Workflow
Agile Workflow
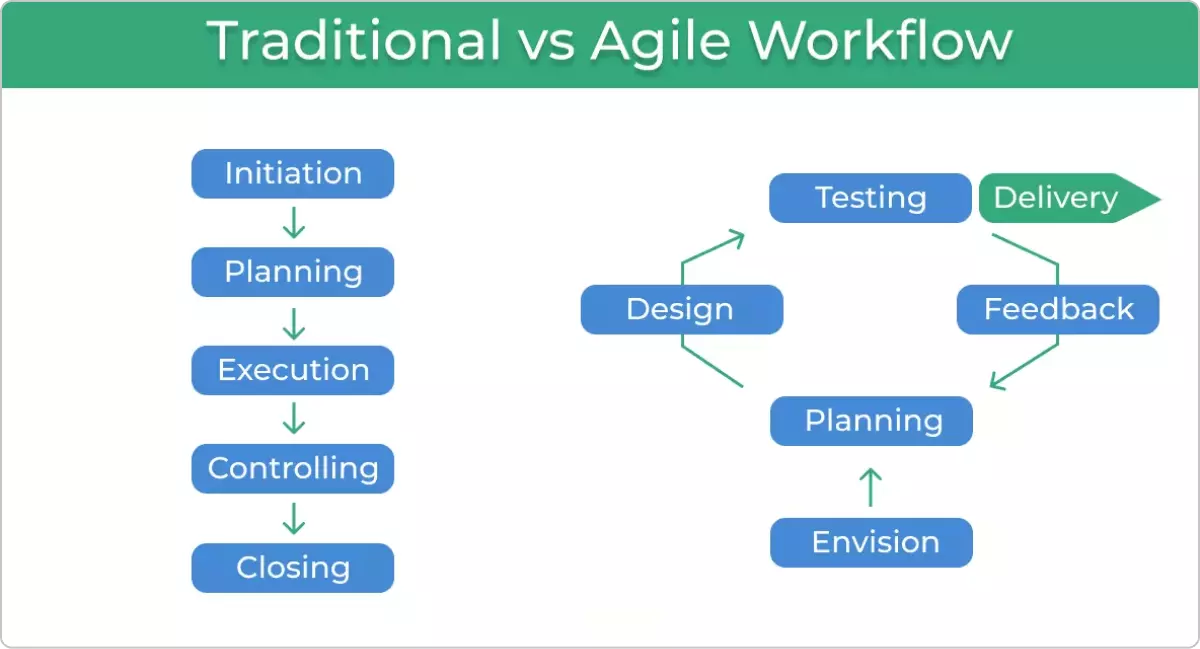
Agile is an iterative approach to project management and software development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. It breaks down projects into smaller increments called iterations, allowing teams to adapt and respond to changes quickly. The Agile Manifesto outlines four core values:
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
Traditional Workflow
Traditional project management methodologies, such as Waterfall, follow a linear, sequential approach. Projects are typically divided into distinct phases (e.g., requirements gathering, design, development, testing) with minimal flexibility for changes once a phase is completed. This rigid structure can lead to challenges in responding to evolving requirements or market conditions.
How an Agile Workflow is Created?
An Agile workflow is characterized by its iterative and collaborative nature. Here's how it's typically created:
1. Project Initiation: The project team defines the project scope, objectives, and initial requirements. Stakeholders are identified, and communication channels are established.
2. Sprint Planning: The project is broken down into smaller iterations called sprints, usually lasting 1-4 weeks. During sprint planning, the team selects items from the product backlog to work on during the sprint and defines the tasks required to complete them.
3. Daily Stand-ups: Daily stand-up meetings are held to discuss progress, challenges, and plans for the day. These short, focused meetings promote transparency and alignment within the team.
4. Iterative Development: Teams work collaboratively to develop and deliver working increments of the product at the end of each sprint. Continuous feedback from stakeholders helps refine and prioritize requirements.
5. Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and gathers feedback. This feedback informs future iterations and ensures alignment with project goals with https://stintar.com.
6. Retrospective: The team reflects on the sprint process, identifies areas for improvement, and implements changes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in subsequent sprints.
Advantages of Agile Workflow
Agile offers several advantages over traditional workflows, including:
1. Flexibility: Agile allows teams to adapt to changing requirements and market conditions quickly.
2. Faster Time to Market: By delivering working increments of the product at the end of each sprint, Agile enables faster delivery of value to customers.
3. Enhanced Collaboration: Agile promotes collaboration among cross-functional teams, fostering a culture of transparency and shared responsibility.
4. Improved Quality: Continuous feedback and iterative development lead to higher-quality outcomes and reduced risk of project failure.
5. Increased Stakeholder Satisfaction: Regular stakeholder involvement ensures that the delivered product meets their needs and expectations.
Optimizing Agile Workflow with Stintar
Stintar is a project management tool designed to streamline Agile workflows and maximize team productivity. It offers features such as:
Sprint Planning: Easily plan and prioritize tasks for each sprint, ensuring that team members stay focused on the most critical objectives.
Collaboration Tools: Facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, whether they're co-located or distributed across different locations.
Task Tracking: Monitor progress in real-time and identify potential bottlenecks or tasks early on, allowing for timely adjustments.
Feedback Mechanisms: Gather feedback from stakeholders and team members to continuously improve processes and deliverables.
In conclusion, Agile and traditional workflows represent two distinct approaches to project management, each with its own strengths and limitations. While traditional workflows offer stability and predictability, Agile provides flexibility and adaptability in a rapidly changing environment. By leveraging tools like Stintar, teams can optimize their Agile workflows, streamline collaboration, and deliver value to stakeholders more effectively. Embracing Agile methodologies and harnessing the power of innovative tools like Stintar can help organizations stay competitive in today's dynamic business landscape.