In-Depth Overview Of The 5 Phases Of Project Management Life Cycle
Regardless of your industry or the company you work for, understanding the project management cycle is essential. Effective project management requires ensuring that each task is successfully completed on time, which demands vigilance and meticulous attention to detail.
To guarantee that all processes within a project are executed flawlessly, it's crucial to follow the phases of the project management life cycle. Being attentive to these stages ensures that every aspect of the project runs smoothly and stays on track.
In this article, we will delve into the five phases of the project management life cycle. But first, let's define what the project life cycle entails.
What Is the Project Life Cycle?
The project life cycle is a structured five-phase process that helps project managers efficiently manage projects from inception to completion. Successfully navigating each phase brings you closer to achieving your project goals.
Phases of the Project Management Life Cycle
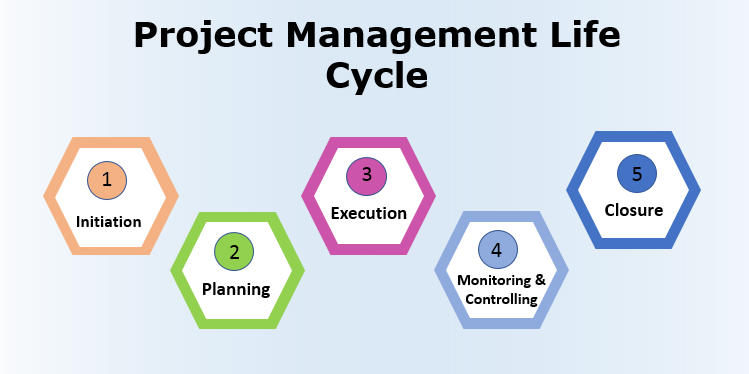
There are five key stages in the project management cycle:
1. Initiation: This phase sets the foundation by defining the project's purpose and objectives.
2. Planning: Detailed planning creates a roadmap for how the project will be executed and controlled.
3. Execution: This stage focuses on delivering the project outputs.
4. Monitoring and Controlling: Continuous tracking ensures the project remains on track and meets its goals.
5. Closing: The final phase concludes the project, ensuring all deliverables are completed and lessons learned are documented.
Project management is a vital aspect of any successful business. It involves organizing, planning, and executing projects efficiently and effectively. The project management life cycle consists of five distinct phases that guide a project from conception to completion. Understanding and implementing these phases can significantly enhance the success rate of projects.
1. Initiation Phase
The initiation phase marks the beginning of a project. This phase is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire project. The main goal here is to define the project at a broad level and determine whether the project is feasible and should be undertaken.
Key Activities in the Initiation Phase
Developing a Project Charter: The project charter is a document that formally authorizes the project. It includes the project’s purpose, objectives, and stakeholders.
Identifying Stakeholders: Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have an interest in the project's outcome. Identifying stakeholders early on ensures their needs and expectations are considered.
Feasibility Study: This involves assessing the practicality of the project. It includes an analysis of technical, financial, and operational feasibility.
Defining the Project Scope: The scope outlines what the project will achieve and the work required to complete it. This helps prevent scope creep (uncontrolled changes or continuous growth in a project’s scope).
Outputs of the Initiation Phase:
Project Charter
Stakeholder Register
Feasibility Study Report
Preliminary Scope Statement
2. Planning Phase
Once the project is approved in the initiation phase, it moves into the planning phase. This phase involves detailed planning to ensure the project is completed on time, within budget, and meets the required quality standards.
Key Activities in the Planning Phase:
Developing a Project Management Plan: This comprehensive document outlines how the project will be executed, monitored, and controlled. It includes subsidiary plans such as scope management, schedule management, cost management, quality management, resource management, communication management, risk management, procurement management, and stakeholder management.
Defining Activities and Sequencing: Breaking down the project into smaller tasks and determining the sequence in which they should be performed.
Estimating Resources and Duration: Estimating the resources (human, financial, material) required and the time needed to complete each task.
Developing a Schedule: Creating a detailed project schedule using tools like Gantt charts and critical path method (CPM).
Risk Management Planning: Identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and developing mitigation strategies.
Outputs of the Planning Phase:
Project Management Plan
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Project Schedule
Cost Estimates
Risk Management Plan
3. Execution Phase
The execution phase is where the project plan is put into action. This phase involves coordinating people and resources to carry out the project plan and produce the project deliverables.
Key Activities in the Execution Phase:
Executing the Project Plan: Carrying out the tasks as per the project management plan.
Resource Allocation: Assigning the right resources to the right tasks at the right time.
Managing Teams: Leading and managing the project team to ensure high performance.
Quality Assurance: Ensuring the project's deliverables meet the required quality standards.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Keeping stakeholders informed and engaged through regular updates and meetings.
Procurement Management: Managing contracts and suppliers to ensure timely delivery of goods and services.
Outputs of the Execution Phase:
Project Deliverables
Performance Reports
Change Requests
Quality Reports
4. Monitoring and Controlling Phase
The monitoring and controlling phase occurs simultaneously with the execution phase. Its purpose is to track, review, and regulate the progress and performance of the project and to identify any areas where changes to the plan are required.
Key Activities in the Monitoring and Controlling Phase:
Performance Monitoring: Tracking the progress of the project against the project management plan using key performance indicators (KPIs).
Variance Analysis: Comparing actual performance with planned performance to identify any variances.
Change Control: Managing changes to the project scope, schedule, and costs through a formal change control process.
Quality Control: Ensuring that project deliverables meet the defined quality standards.
Risk Monitoring: Continuously identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks.
Stakeholder Management: Keeping stakeholders informed about the project’s progress and any changes that may affect them.
Outputs of the Monitoring and Controlling Phase:
Performance Reports
Change Log
Quality Control Measurements
Risk Register Updates
Task Log
5. Closing Phase
The closing phase signifies the completion of the project. This phase involves finalizing all activities, handing over the project deliverables to the customer, and formally closing the project.
Key Activities in the Closing Phase:
Finalizing Deliverables: Ensuring all project deliverables are completed and meet the required standards.
Closing Contracts: Finalizing and closing all contracts with suppliers and vendors.
Release of Resources: Releasing project resources and ensuring they are reassigned to other projects or tasks.
Documenting Lessons Learned: Recording any lessons learned during the project to improve future projects.
Post-Project Evaluation: Conducting a final project evaluation to assess the project’s success and identify areas for improvement.
Formal Closure: Formally closing the project by obtaining formal acceptance of the project deliverables from the customer and ensuring all administrative tasks are completed.
Outputs of the Closing Phase:
Final Project Report
Lessons Learned Document
Formal Acceptance Documentation
Archived Project Documents
Stintar: Your ultimate tool for Project Management Software
Navigating the various phases of the project management life cycle can be quite daunting, especially when you have multiple responsibilities to manage. If keeping up with the project management process feels overwhelming, consider signing up for Stintar.
Stintar is a comprehensive project management tool integrated with CRM and HRM functionalities that are designed to streamline your project management tasks. It enables you to create detailed workflows by breaking projects down into manageable tasks. Each task is assigned to a specific resource with a clear deadline, ensuring accountability and efficiency. Additionally, you can easily schedule meetings with your team whenever needed.
Stintar also features robust task tracking, sales management, lead management, client management, file manager, knowledge base, and payroll management modules, which help you quickly identify and address potential threats. Moreover, it fosters seamless collaboration among team members, making project management smoother and more effective. Stintar also offers a 1 year free trial for up to 5 users. So why wait and sign up now at www.stintar.com and enjoy the Stintar tool for your business success.
Conclusion
The project management life cycle is a vital framework that guides project managers through the complexities of a project. By understanding and applying the five phases – Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closing – project managers can ensure their projects are well-organized, efficiently managed, and successfully completed.
Each phase plays a crucial role in the overall success of the project. The initiation phase sets the stage by defining the project's purpose and objectives. The planning phase creates a detailed roadmap for execution and control. The execution phase is all about delivering the project outputs, while the monitoring and controlling phase ensures the project stays on track and meets its goals. Finally, the closing phase concludes the project, ensuring all deliverables are finalized and lessons learned are documented.
By adhering to this structured approach, project managers can significantly increase the chances of delivering successful projects that meet or exceed stakeholder expectations. Whether managing a small project or a large, complex one, following the project management life cycle provides the clarity and direction needed to navigate through each stage effectively. For added support and efficiency, consider using Stintar, a powerful project management tool designed to streamline your workflow and enhance collaboration.